Development of a TB Treatment Compliance Instrument using the Health Belief Model
https://doi.org/10.33860/jik.v19i1.3883
Keywords:
TB Paru, Health belief model, instrumentAbstract
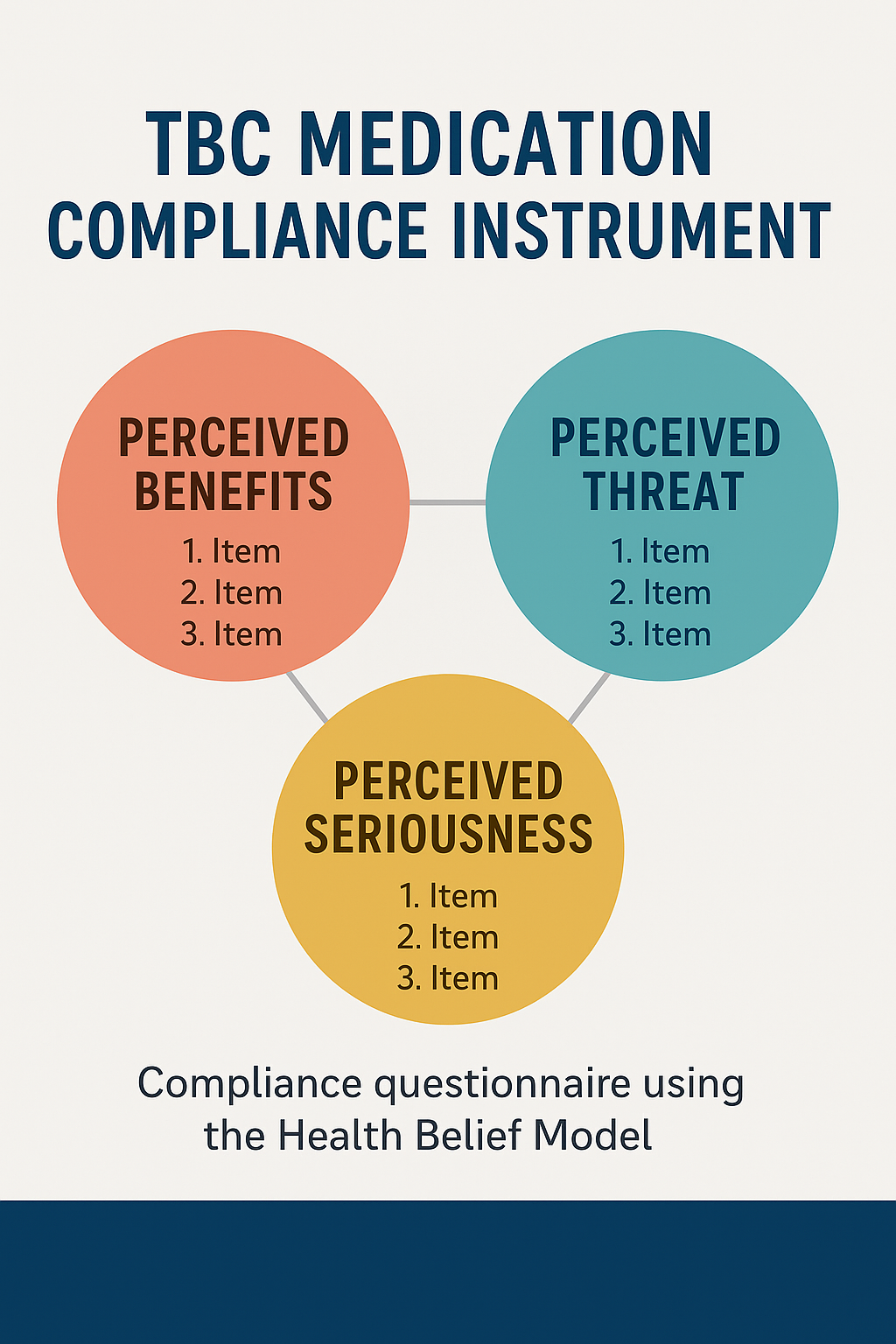
Several things that influence patient non-compliance in undergoing treatment include the length of treatment, in addition, there are drug factors, diseases and patients.Another fact is the lack of attention from the government and the patients themselves because even though free treatment is available. Aim of the study was to compile a TBC medication complient instrumen. The method using surveyThe sample was TB patients in Palu City, namely at the Talise Health Center, and in Donggala Regency, namely the Wani Health Center and the Gonenggati Donggala Health Center. The sample that participated in this study was 69 people. The analysis technique used was multidimensional confirmatory factor analysis (SEM). 20 question items were obtained from this study. Compliance questionnaires using the health belief model can be used to measure TB patient compliance with treatment. consisting of 3 assessment items; perceived benefit, perceived threat, perception of seriousness and threat. Compliance questionnaires using the health belief model can be used to measure TB patient compliance with treatment.
References
1. Yuni IDAMA. Hubungan Fase pengobatan TB dan pengetahuan tentang MDR TB dengan kepatuhan pengobatan pasien TB (Studi di Puskesmas Perak Timur). J Berk Epidemiol. 2016;4(3):384–95. https://e-journal.unair.ac.id/JBE/article/download/2015/2540
2. Kemenkes. Laporan Program Penanggulangan Tuberkulosis. 2021. 157 p. https://repository.kemkes.go.id/book/1288
3. WHO. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Who. 2020. 1–120 p. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240107243
4. Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Survey Kesehatan Indonesia (SKI) tahun 2023. Vol. 01. 2024. https://kemkes.go.id/id/survei-kesehatan-indonesia-ski-2023
5. Kemenkes. Modul 4b diagnosis tuberkulosis pada dewasa. 2023;
6. Fitri LD. Kepatuhan Minum Obat pada Pasien Tuberkulosis Paru. J Ilmu Kesehat Masy. 2018;7(01):33–42. https://journals.stikim.ac.id/index.php/jikm/article/download/50/42
7. Pameswari P, Halim A, Yustika L. Tingkat Kepatuhan Penggunaan Obat pada Pasien Tuberkulosis di Rumah Sakit Mayjen H. A Thalib Kabupaten Kerinci. J Sains Farm Klin. 2016;2(2):116.
8. Putri NCHP, Rahmawati, Maftukhin A. Gambaran Implementasi Teori HBM (Health Belief Model) dalam Perilaku Penanganan Fraktur ke Sangka Putung Mbah Jajar Sukosewu. J llmiah Kesehat. 2024;4(1):5–13. https://ejournal.rajekwesi.ac.id/index.php/Kesehatan/article/view/429
9. Sastroasmoro S, Ismael S. Dasar-dasar metodologi penelitian klinis. 5th ed. Jakarta: Sagung Seto; 2014. 522 p.
10. Kemenkes RI. Penemuan Kasus ILTB Tujuan Pembelajaran. 2022. https://www.tbindonesia.or.id/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Isi-Juknis-ILTB-FINAL-ok_published.pdf
11. Ulfah U, Windiyaningsih C, Abidin Z, Murtiani F. Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Kepatuhan Berobat Pada Penderita Tuberkulosis Paru. Indones J Infect Dis. 2018;4(1).
12. Humaidi F, Anggarini DR, Madura UI, Madura UI. Kepatuhan Minum Obat Anti Tuberkulosis Pada Pasien TBC Regimen. J Ilm Farm Attaamru. 2020;01(01). https://journal.uim.ac.id/index.php/Attamru/article/download/917/598/
13. Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Modul Pelatihan Infeksi Laten Tuberkulosis (Iltb) Dan Terapi Pencegahan Tuberkulosis (Tpt). Modul 1 Epidemiol Tuberkulosis. 2022;
14. Kementrian Kesehatan RI. Pedoman Nasional Pelayanan Kedokteran Tata laksana Tuberkulosis. 2020.
15. Ahdiyah NN, Andriani M, Andriani L. Tingkat Kepatuhan Penggunaan Obat Anti Tuberkulosis Pada Pasien TB Paru Dewasa Di Puskesmas Putri Ayu. Lumbung Farm J Ilmu Kefarmasian. 2022;3(1):23. https://journal.ummat.ac.id/index.php/farmasi/article/view/6817
16. Tuty Putri S, Adikusuma Suparto T, DIII Keperawatan P. Gambaran Kepatuhan Pasien Tuberkulosis Paru Terhadap Regimen Terapeutik Di Puskesmas Padasuka Kota Bandung. J Pendidik Keperawatan Indones. 2015;1(2). https://ejournal.upi.edu/index.php/JPKI/article/view/9747
17. Green EC, Murphy EM, Gryboski K. The Health Belief Model. Wiley Encycl Heal Psychol. 2020;(May 2022):211–4. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781119057840.ch68
18. Home Visiting Applied Research Collaborative. Health Belief Modle. 2023; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK606120/
19. Magdalena T. Bolon C, Viska Renata Pasaribu, Rostinah Manurung, Paskah Rina Situmorang. Efektivitas Pemberian Kesehatan The Health Belief Model Terhadap Pengetahuan Keluarga Tentang Tb Paru Di Rs Tni Al Dr. Komang Makes Belawan. J Ilm Keperawatan Imelda. 2021;7(2):137–41. https://jurnal.uimedan.ac.id/index.php/JURNALKEPERAWATAN/article/view/530
20. Fitriyani L, Dwijayanti F, Studi Sarjana Terapan Manajemen Informasi Kesehatan P, Ilmu Kesehatan F, Kesehatan dan Teknologi PKP DKI Jakarta I. Edukasi Teori Health Belief Model Pada Pasien Tuberkulosis Di Kecamatan Pancoran Mas Kota Depok. Communnity Dev J. 2023;4(2):2586–9. https://journal.universitaspahlawan.ac.id/index.php/cdj/article/view/14498
21. Widiharti, Jerita Eka Sari D, Suminar E, Laily Rahmah A, Kholidatur Rizkiyah C, Mayreela D. Pemberian Edukasi Perilaku Pencegahan Penularan Tbc Dengan Pendekatan Health Belief Model. MARTABE J Pengabdi Masy. 2022;5(8):2872–6. http://jurnal.um-tapsel.ac.id/index.php/martabe/article/view/8102
22. Yuli Irnawati, Fery Rahmawati. Implementasi Teori HBM (Health Belief Model) dalam Pencegahan Perilaku Hiv/Aids pada Wanita Usia Subur (WUS). J Pengemas Kesehat. 2022;1(01):13–7. https://jpk.stikesbup.ac.id/index.php/jpk/article/view/3
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with Poltekita : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License.
Poltekita : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.






