Water, Hygiene, and Sanitation Risk Factors towards Stunting among Children (0-14 years): A Systematic Literature Review
https://doi.org/10.33860/bpk.v53i2.4044
Keywords:
WASH, Sanitation, Hygiene, Child, StuntingAbstract
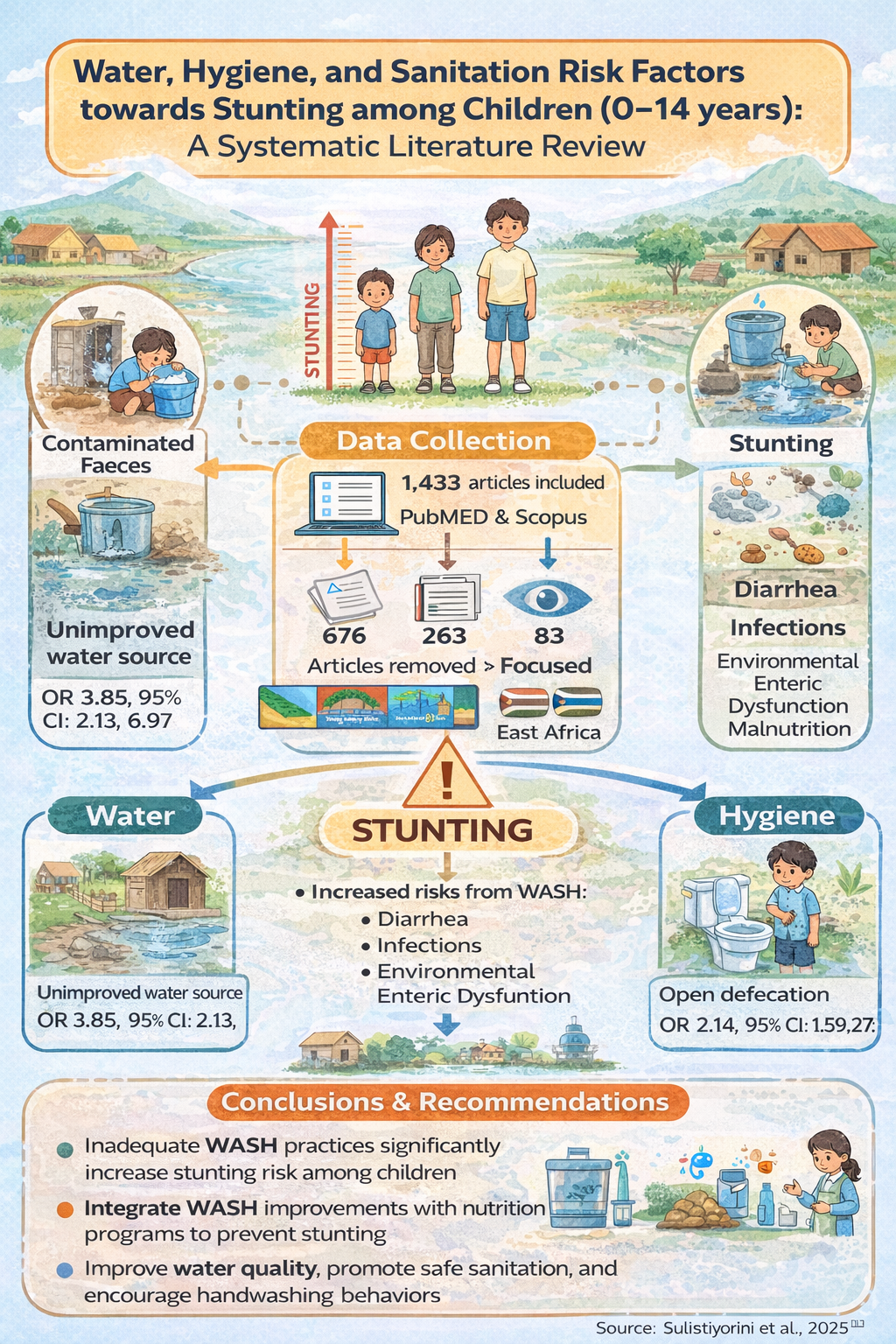
Background: Stunting remains a major public health problem in low- and middle-income countries and is closely linked to inadequate water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) conditions through repeated infections and impaired nutrient absorption. Evidence on the role of WASH across a broader child age range remains limited. This study aimed to systematically review the association between WASH factors and stunting among children aged 0–14 years.
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted following PRISMA guidelines. Articles published in English between 2013 and 2023 were retrieved from PubMed and Scopus using the keywords “water,” “sanitation,” “hygiene,” “WASH,” and “stunting.” Observational studies conducted in low- and middle-income countries were included. Two reviewers independently screened titles, abstracts, and full texts.
Results: A total of 83 studies were included, predominantly cross-sectional in design. Most studies were conducted in East Africa and Southeast Asia. Consistent evidence showed that unimproved water sources, lack of water treatment, poor sanitation facilities, open defecation, unsafe disposal of child feces, and inadequate hygiene practices—particularly handwashing—were significantly associated with increased risk of stunting. Improved water access, sanitation infrastructure, and hygiene behaviors were identified as protective factors.
Conclusion: Inadequate WASH conditions are strongly associated with childhood stunting. Integrating WASH interventions, especially sanitation and hygiene improvements, with nutrition programs is essential to reduce stunting and promote healthy child growth in low- and middle-income countries.
Downloads
References
Ademas, A., Adane, M., Keleb, A., Berihun, G., & Tesfaw, G. (2021). Water, sanitation, and hygiene as a priority intervention for stunting in under-five children in northwest Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 47(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-021-01128-y
Aguayo, V. M., Nair, R., Badgaiyan, N., & Krishna, V. (2016). Determinants of stunting and poor linear growth in children under 2 years of age in India: an in-depth analysis of Maharashtra’s comprehensive nutrition survey. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), 121–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12259
Ahmad, S., Abid, J., Muhammad, N., Wasila, H., Zaitoun, M., & Awudi, D. A. (2022). Prevalence and factors associated with undernutrition among 6-59 months children in Tehsil Battagram, Pakistan. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, 72(8), 1535–1543. https://doi.org/10.47391/JPMA.3867
Ahmed, N. A. M. F., Sultana, M., & Ali, M. (2021). Identifying the factors causing malnutrition and its impact on mortality among under-five Bangladeshi children. 23(3), 255–260.
Ainy, F. N., Susanto, T., & Susumaningrum, L. A. (2021). The relationship between environmental sanitation of family and stunting among under-five children: A cross-sectional study in the public health center of jember, indonesia. Nursing Practice Today, 8(3), 173–178. https://doi.org/10.18502/npt.v8i3.5932
Altare, C., Delbiso, T. D., Mutwiri, G. M., Kopplow, R., & Guha-Sapir, D. (2016). Factors Associated with Stunting among Pre-school Children in Southern Highlands of Tanzania. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 62(5), 390–408. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmw024
Amare, H. H., & Lindtjorn, B. (2021a). Concurrent anemia and stunting among schoolchildren in Wonago district in southern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional multilevel analysis. PeerJ, 9. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.11158
Amare, H. H., & Lindtjorn, B. (2021b). Concurrent anemia and stunting among schoolchildren in Wonago district in southern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional multilevel analysis. PeerJ, 9. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.11158
Amare, Z. Y., Ahmed, M. E., & Mehari, A. B. (2019). Determinants of nutritional status among children under age 5 in Ethiopia: Further analysis of the 2016 Ethiopia demographic and health survey. Globalization and Health, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-019-0505-7
Astuti, D. D., Handayani, T. W., & Astuti, D. P. (2020). Cigarette smoke exposure and increased risks of stunting among under-five children. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health, 8(3), 943–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2020.02.029
Bauza, V., & Guest, J. S. (2017). The effect of young children’s faeces disposal practices on child growth: evidence from 34 countries. Tropical Medicine and International Health, 22(10), 1233–1248. https://doi.org/10.1111/tmi.12930
Bazie, G. W., Seid, M., & Egata, G. (2021). Prevalence and Predictors of Stunting among Primary School Children in Northeast Ethiopia. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8876851
Beal, T., Tumilowicz, A., Sutrisna, A., Izwardy, D., & Neufeld, L. M. (2018). A review of child stunting determinants in Indonesia. Maternal and Child Nutrition, 14(4), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12617
Bekele, T., Rahman, B., & Rawstorne, P. (2020). The effect of access to water, sanitation and handwashing facilities on child growth indicators: Evidence from the Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2016. PLoS ONE, 15(9 September). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239313
Berawi, K. N., Puspaningrum, D. A., Bakri, S., Zuraida, R., Kurniawaty, E., & Yanfika, H. (2023). The Effect of Sanitation Performance and Parental Livelihood on Stunting Severity: Study at 3 Ecological Zones at South Lampung Regency, Indonesia. Universal Journal of Public Health, 11(1), 155–169. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujph.2023.110117
Berhanu, A., Garoma, S., Arero, G., & Mosisa, G. (2022). Stunting and associated factors among school-age children (5–14 years) in Mulo district, Oromia region, Ethiopia. SAGE Open Medicine, 10. https://doi.org/10.1177/20503121221127880
Berhanu, G., Mekonnen, S., & Sisay, M. (2018). Prevalence of stunting and associated factors among preschool children: A community based comparative cross sectional study in Ethiopia. BMC Nutrition, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-018-0236-9
Capanzana, M. V, Aguila, D. V, Gironella, G. M. P., & Montecillo, K. V. (2018). Nutritional status of children ages 0-5 and 5-10 years old in households headed by fisherfolks in the Philippines. Archives of Public Health, 76(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-018-0267-3
Christian, A. K., Afful-Dadzie, E., & Marquis, G. S. (2023). Infant and young child feeding practices are associated with childhood anaemia and stunting in sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Nutrition, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-022-00667-9
Cumming, O., & Cairncross, S. (2016). Can water, sanitation and hygiene help eliminate stunting? Current evidence and policy implications. Maternal and Child Nutrition, 12, 91–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12258
Das, M., Verma, M., Sahoo, S. S., & Gupta, M. (2022). Regional Water Availability and WASH Indicators as Predictors of Malnutrition in Under-5 Children: Analysis of the National Family Health Survey, India (2015-16). Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 68(3). https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmac030
Das, S., Fahim, S. M., Alam, M. A., Mahfuz, M., Bessong, P., Mduma, E., Kosek, M., Shrestha, S. K., & Ahmed, T. (2021). Not water, sanitation and hygiene practice, but timing of stunting is associated with recovery from stunting at 24 months: Results from a multi-country birth cohort study. Public Health Nutrition, 24(6), 1428–1437. https://doi.org/10.1017/S136898002000004X
De Vita, M. V, Scolfaro, C., Santini, B., Lezo, A., Gobbi, F., Buonfrate, D., Kimani-Murage, E. W., Macharia, T., Wanjohi, M., Rovarini, J. M., & Morino, G. (2019). Malnutrition, morbidity and infection in the informal settlements of Nairobi, Kenya: An epidemiological study. Italian Journal of Pediatrics, 45(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-019-0607-0
Dearden, K. A., Schott, W., Crookston, B. T., Humphries, D. L., Penny, M. E., & Behrman, J. R. (2017). Children with access to improved sanitation but not improved water are at lower risk of stunting compared to children without access: a cohort study in Ethiopia, India, Peru, and Vietnam. BMC Public Health, 17(1), 110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4033-1
Demilew, Y. M., & Alem, A. T. (2019). Food security is not the only solution to prevent under-nutrition among 6-59 months old children in Western Amhara region, Ethiopia. BMC Pediatrics, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1386-2
Demirchyan, A., Petrosyan, V., Sargsyan, V., & Hekimian, K. (2016). Predictors of Stunting Among Children Ages 0 to 59 Months in a Rural Region of Armenia. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 62(1), 150–156. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000000901
Dominguez-Salas, P., Waddington, H. S., Grace, D., Bosire, C., Moodley, A., Kulkarni, B., Dasi, T., Banjara, S. K., Kumar, R. N., Fahmida, U., Htet, M. K., Sudibya, A. R. P., Faye, B., Tine, R. C., Heffernan, C., Saxena, D., Dreibelbis, R., & Häsler, B. (2024). Understanding the role of household hygiene practices and foodborne disease risks in child stunting: A UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub protocol paper. BMJ Paediatrics Open, 8(Suppl 1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjpo-2022-001695
Fadjriah, R. N., Rusdianto, R., Herman, H., & Vidyanto, V. (2021). Factors associated with the stunting in toddlers in the work area of tikson raya public health center. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 9, 1207–1212. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2021.6957
Faisal Ahmed, N. A. M., Sultana, M., Ali, M., Abedin, M. M., Ahammed, B., Yeasmin, M. A., & Maniruzzaman, M. (2021). Identifying the factors causing malnutrition and its impact on mortality among under-five bangladeshi children. Family Medicine and Primary Care Review, 23(3), 255–260. https://doi.org/10.5114/fmpcr.2021.108185
Farah, A. M., Nour, T. Y., Endris, B. S., & Gebreyesus, S. H. (2021). Concurrence of stunting and overweight/obesity among children: Evidence from Ethiopia. PloS One, 16(1), e0245456. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245456
Fernandes, E. C. B., de Castro, T. G., & Sartorelli, D. S. (2017). Associated factors of malnutrition among African children under five years old, Bom Jesus, Angola. Revista de Nutricao, 30(1), 33–44. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-98652017000100004
Fuller, J. A., Villamor, E., Cevallos, W., Trostle, J., & Eisenberg, J. N. (2016). I get height with a little help from my friends: herd protection from sanitation on child growth in rural Ecuador. International Journal of Epidemiology, 45(2), 460–469. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv368
Gaffan, N., Kpozehouen, A., Degbey, C., Ahanhanzo, Y. G., & Paraïso, M. N. (2023). Effects of the level of household access to water, sanitation and hygiene on the nutritional status of children under five, Benin. BMC Nutrition, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-023-00751-8
Garcia, S., Sarmiento, O. L., Forde, I., & Velasco, T. (2013). Socio-economic inequalities in malnutrition among children and adolescents in Colombia: the role of individual-, household- and community-level characteristics. Public Health Nutrition, 16(9), 1703–1718. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980012004090
Gebru, T. T., Tesfamichael, Y. A., Bitow, M. T., Assefa, N. E., Abady, G. G., Mengesha, M. B., & Gebremedhin, H. T. (2019). Stunting and associated factors among under-five children in Wukro town, Tigray region, Ethiopia: A cross sectional study. BMC Research Notes, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4535-2
Geletaw, A., Egata, G., Weldegebreal, F., Kibr, G., & Semaw, M. (2021). Nutritional Status and Associated Factors among Primary Schoolchildren from Pastoral Communities, Mieso-Mulu District, Sitti Zone, Somali Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia: Institution-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6630620
Girma, A., Woldie, H., Mekonnen, F. A., Gonete, K. A., & Sisay, M. (2019). Undernutrition and associated factors among urban children aged 24-59 months in Northwest Ethiopia: A community based cross sectional study. BMC Pediatrics, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-019-1595-3
Gizaw, Z., Yalew, A. W., Bitew, B. D., Lee, J., & Bisesi, M. (2022). Stunting among children aged 24–59 months and associations with sanitation, enteric infections, and environmental enteric dysfunction in rural northwest Ethiopia. Scientific Reports, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23981-5
Haq, W., & Abbas, F. (2022a). A Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated With Stunting in Children Less Than 2 years Using Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) 2017–18 of Punjab, Pakistan. SAGE Open, 12(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221096127
Haq, W., & Abbas, F. (2022b). A Multilevel Analysis of Factors Associated With Stunting in Children Less Than 2 years Using Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) 2017–18 of Punjab, Pakistan. SAGE Open, 12(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221096127
Haque, M. A., Choudhury, N., Wahid, B. Z., Ahmed, S. T., Farzana, F. D., Ali, M., Naz, F., Siddiqua, T. J., Rahman, S. S., Faruque, A. S. G., & Ahmed, T. (2023). A predictive modelling approach to illustrate factors correlating with stunting among children aged 12-23 months: a cluster randomised pre-post study. BMJ Open, 13(4), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067961
Hasan, M. M., Asif, C. A. A., Barua, A., Banerjee, A., Kalam, M. A., Kader, A., Wahed, T., Noman, M. W., & Talukder, A. (2023a). Association of access to water, sanitation and handwashing facilities with undernutrition of children below 5 years of age in Bangladesh: Evidence from two population-based, nationally representative surveys. BMJ Open, 13(6). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065330
Hasan, M. M., Asif, C. A. A., Barua, A., Banerjee, A., Kalam, M. A., Kader, A., Wahed, T., Noman, M. W., & Talukder, A. (2023b). Association of access to water, sanitation and handwashing facilities with undernutrition of children below 5 years of age in Bangladesh: Evidence from two population-based, nationally representative surveys. BMJ Open, 13(6). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065330
Hasanah, U., Maria, I. L., Jafar, N., Hardianti, A., Mallongi, A., & Syam, A. (2020). Water, sanitation dan hygiene analysis, and individual factors for stunting among children under two years in ambon. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 8(T2), 22–26. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2020.5177
Heller, L., & Carneiro, M. (2023). WASH and health: from global estimates to whys and hows. The Lancet, 401(10393), 2017–2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00765-1
Hiliza, J. N., Germana, L., Kasangala, A., & Joram, F. (2020). Prevalence and Factors Associated with Stunting among Public Primary School Pupils in Kasulu District, Western Tanzania. The East African Health Research Journal, 4(2), 172–181. https://doi.org/10.24248/eahrj.v4i2.641
Horta, B. L., Santos, R. V., Welch, J. R., Cardoso, A. M., dos Santos, J. V., Assis, A. M. O., Lira, P. C. I., & Coimbra, C. E. A. J. (2013). Nutritional status of indigenous children: findings from the First National Survey of Indigenous People’s Health and Nutrition in Brazil. International Journal for Equity in Health, 12, 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-12-23
Htet, M. K., Do, T. T., Wah, T., Zin, T., Hmone, M. P., Raihana, S., Kirkwood, E., Hlaing, L. M., & Dibley, M. J. (2023). Socio-economic and agricultural factors associated with stunting of under 5-year children: Findings from surveys in mountains, dry zone and delta regions of rural Myanmar (2016-2017). Public Health Nutrition, 26(8), 1644–1657. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980023001076
Ikeda, N., Irie, Y., & Shibuya, K. (2013). Determinants of reduced child stunting in Cambodia: analysis of pooled data from three demographic and health surveys. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 91(5), 341–349. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.12.113381
Ishwarji, M. I., Rao, K. M., Ramakrishna, K. S., Kumar, R. H., Venkaiah, K., & Laxmaiah, A. (2019). Regional variation in the prevalence of undernutrition and its correlates among under 5 year children in western india. Indian Journal of Community Health, 31(4), 521–531. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85082130149&partnerID=40&md5=5c34f4fa4c1668ee7ab573ead838576f
Janawisuta, H., & Gunawan, P. H. (2024). Early Detection of Stunting in Indonesian Toddlers: A Machine Learning Approach. 2024 International Conference on Data Science and Its Applications, ICoDSA 2024, 12–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICoDSA62899.2024.10651637
Kasajja, M., Nabiwemba, E., Wamani, H., & Kamukama, S. (2022). Prevalence and factors associated with stunting among children aged 6–59 months in Kabale district, Uganda. BMC Nutrition, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-022-00578-9
Kebede, D., & Aynalem, A. (2021). Prevalence of undernutrition and potential risk factors among children below five years of age in Somali region, Ethiopia: evidence from 2016 Ethiopian demographic and health survey. BMC Nutrition, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-021-00460-0
Kismul, H., Acharya, P., Mapatano, M. A., & Hatløy, A. (2017). Determinants of childhood stunting in the Democratic Republic of Congo: further analysis of Demographic and Health Survey 2013-14. BMC Public Health, 18(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4621-0
Lai, A., Velez, I., Ambikapathi, R., Seng, K., Cumming, O., & Brown, J. (2022a). Risk factors for early childhood growth faltering in rural Cambodia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open, 12(4), e058092. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058092
Lai, A., Velez, I., Ambikapathi, R., Seng, K., Cumming, O., & Brown, J. (2022b). Risk factors for early childhood growth faltering in rural Cambodia: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open, 12(4), e058092. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058092
Lee, C., Lakhanpaul, M., Stern, B. M., Sarkar, K., & Parikh, P. (2021). Associations between the household environment and stunted child growth in rural India: a cross-sectional analysis. UCL Open. Environment, 3, e014. https://doi.org/10.14324/111.444/ucloe.000014
Lin, J., & Feng, X. L. (2023). Exploring the impact of water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH), early adequate feeding and access to health care on urban–rural disparities of child malnutrition in China. Maternal & Child Nutrition, June, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.13542
Mahmood, T., Abbas, F., Kumar, R., & Somrongthong, R. (2020). Why under five children are stunted in Pakistan? A multilevel analysis of Punjab Multiple indicator Cluster Survey (MICS-2014). BMC Public Health, 20(1), 952. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09110-9
Makasi, R. R., & Humphrey, J. H. (2020). Summarizing the Child Growth and Diarrhea Findings of the Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Benefits and Sanitation Hygiene Infant Nutrition Efficacy Trials. Nestle Nutrition Institute Workshop Series, 93, 153–166. https://doi.org/10.1159/000503350
Malako, B. G., Asamoah, B. O., Tadesse, M., Hussen, R., & Gebre, M. T. (2019). Stunting and anemia among children 6-23 months old in Damot Sore district, Southern Ethiopia. BMC Nutrition, 5(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-018-0268-1
Meierhofer, R., Kunwar, B. M., & Shrestha, A. (2023). Changes in water treatment, hygiene practices, household floors, and child health in times of Covid-19: A longitudinal cross-sectional survey in Surkhet District, Nepal. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2023.114138
Mertens, A., Arnold, B. F., Benjamin-Chung, J., Boehm, A. B., Brown, J., Capone, D., Clasen, T., Fuhrmeister, E. R., Grembi, J. A., Holcomb, D., Knee, J., Kwong, L. H., Lin, A., Luby, S. P., Nala, R., Nelson, K., Njenga, S. M., Null, C., Pickering, A. J., … Ercumen, A. (2024). Is detection of enteropathogens and human or animal faecal markers in the environment associated with subsequent child enteric infections and growth: an individual participant data meta-analysis. The Lancet Global Health, 12(3), e433–e444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00563-6
Meshram, I. I., Kodavanti, M. R., Chitty, G. R., Manchala, R., Kumar, S., Kakani, S. K., Kodavalla, V., Avula, L., & Ginnela Narsimhachary Veera, B. (2015). Influence of feeding practices and associated factors on the nutritional status of infants in rural areas of Madhya Pradesh State, India. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health, 27(2), NP1345–NP1361. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010539513486174
Mistry, S. K., Hossain, M. B., Khanam, F., Akter, F., Parvez, M., Yunus, F. M., Afsana, K., & Rahman, M. (2019). Individual, maternal- and household-level factors associated with stunting among children aged 0-23 months in Bangladesh. Public Health Nutrition, 22(1), 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980018002926
Modern, G., Sauli, E., & Mpolya, E. (2020). Correlates of diarrhea and stunting among under-five children in Ruvuma, Tanzania; a hospital-based cross-sectional study. Scientific African, 8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00430
Morrison, A. L., Lewthwaite, H., Houghton, L. A., Nasak, D. S. J., Sharples, K. J., Brown, P., Crump, J. A., & Jack, S. J. (2020). Child undernutrition in households with microbiologically safer drinking water and “improved water” in Tanna, Vanuatu. Journal of Water and Health, 18(3), 416–429. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2020.262
Mshida, H. A., Kassim, N., Mpolya, E., & Kimanya, M. (2018). Water, sanitation, and hygiene practices associated with nutritional status of under-five children in semi-pastoral communities Tanzania. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 98(5), 1242–1249. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.17-0399
Muche, A., Gezie, L. D., Baraki, A. G.-E., & Amsalu, E. T. (2021). Predictors of stunting among children age 6–59 months in Ethiopia using Bayesian multi-level analysis. Scientific Reports, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82755-7
Mudadu Silva, J. R., Vieira, L. L., Murta Abreu, A. R., de Souza Fernandes, E., Moreira, T. R., Dias da Costa, G., & Mitre Cotta, R. M. (2023). Water, sanitation, and hygiene vulnerability in child stunting in developing countries: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Public Health, 219(September), 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2023.03.024
Mugarura, D., Ninsiima, H. I., Kinyi, H., Eze, E. D., Tumwesigire, S., Mbekeeka, P., & Ndamira, A. (2021). High-Prevalence Stunting in Preschool Children (1-5 Years) Attending Selected Health Centers in a Food Rich Area-Bushenyi District Southwestern Uganda. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5736864
Mulu, N., Mohammed, B., Woldie, H., & Shitu, K. (2022). Determinants of stunting and wasting in street children in Northwest Ethiopia: A community-based study. Nutrition, 94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111532
Mulyaningsih, T., Mohanty, I., Widyaningsih, V., Gebremedhin, T. A., Miranti, R., & Wiyono, V. H. (2021). Beyond personal factors: Multilevel determinants of childhood stunting in Indonesia. PLoS ONE, 16(11 November), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0260265
Murtaza, S. F., Gan, W. Y., Sulaiman, N., & Shariff, Z. M. (2018a). Factors associated with stunting among Orang Asli preschool children in Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Nutrition, 24(2), 215–226. https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85064318123&partnerID=40&md5=68471e1e843ee63771b9924b4b7f00ee
Murtaza, S. F., Gan, W. Y., Sulaiman, N., & Shariff, Z. M. (2018b). Factors associated with stunting among Orang Asli preschool children in Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Nutrition, 24(2), 215–226.
Nadhiroh, S. R., Micheala, F., Tung, S. E. H., & Kustiawan, T. C. (2023). Association between maternal anemia and stunting in infants and children aged 0–60 months: A systematic literature review. Nutrition, 115, 112094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2023.112094
Ngassa, A. B., Meriki, H. D., Mbanga, C. M., Nzefa, L. D., Mbhenyane, X., & Tambe, A. B. (2022a). Key predictors of undernutrition among children 6–59 months in the Buea Health District of the Southwest region of Cameroon: a cross sectional community-based survey. BMC Nutrition, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-022-00646-0
Ngassa, A. B., Meriki, H. D., Mbanga, C. M., Nzefa, L. D., Mbhenyane, X., & Tambe, A. B. (2022b). Key predictors of undernutrition among children 6–59 months in the Buea Health District of the Southwest region of Cameroon: a cross sectional community-based survey. BMC Nutrition, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-022-00646-0
Oginawati, K., Yapfrine, S. J., Fahimah, N., Salami, I. R. S., & Susetyo, S. H. (2023). The associations of heavy metals exposure in water sources to the risk of stunting cases. Emerging Contaminants, 9(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2023.100247
Okidi, L., Ongeng, D., Muliro, P. S., & Matofari, J. W. (2022a). Disparity in prevalence and predictors of undernutrition in children under five among agricultural, pastoral, and agro-pastoral ecological zones of Karamoja sub-region, Uganda: a cross sectional study. BMC Pediatrics, 22(1), 316. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-022-03363-6
Okidi, L., Ongeng, D., Muliro, P. S., & Matofari, J. W. (2022b). Disparity in prevalence and predictors of undernutrition in children under five among agricultural, pastoral, and agro-pastoral ecological zones of Karamoja sub-region, Uganda: a cross sectional study. BMC Pediatrics, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-022-03363-6
Otsuka, Y., Agestika, L., Sintawardani, N., & Yamauchi, T. (2019). Risk factors for undernutrition and diarrhea prevalence in an urban slum in Indonesia: Focus on water, sanitation, and hygiene. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 100(3), 727–732. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.18-0063
Rah, J. H., Cronin, A. A., Badgaiyan, B., Aguayo, V., Coates, S., & Ahmed, S. (2015a). Household sanitation and personal hygiene practices are associated with child stunting in rural India: A cross-sectional analysis of surveys. BMJ Open, 5(2). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005180
Rah, J. H., Cronin, A. A., Badgaiyan, B., Aguayo, V. M., Coates, S., & Ahmed, S. (2015b). Household sanitation and personal hygiene practices are associated with child stunting in rural India: a cross-sectional analysis of surveys. BMJ Open, 5(2), e005180. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005180
Rah, J. H., Sukotjo, S., Badgaiyan, N., Cronin, A. A., & Torlesse, H. (2020). Improved sanitation is associated with reduced child stunting amongst Indonesian children under 3 years of age. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 16 Suppl 2(Suppl 2), e12741. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12741
Rahman, M. M., Kiyu, A., & Seling, N. R. (2021). Prevalence and factors associated with undernutrition among Dayak children in rural areas of Sarawak, Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Nutrition, 27(3), 433–448. https://doi.org/10.31246/mjn-2021-0045
Reese, H., Sinharoy, S. S., & Clasen, T. (2019). Using structural equation modelling to untangle sanitation, water and hygiene pathways for intervention improvements in height-for-age in children <5 years old. International Journal of Epidemiology, 48(6), 1992–2000. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyz202
Roba, A. A., Assefa, N., Dessie, Y., Tolera, A., Teji, K., Elena, H., Bliznashka, L., & Fawzi, W. (2021). Prevalence and determinants of concurrent wasting and stunting and other indicators of malnutrition among children 6–59 months old in Kersa, Ethiopia. Maternal and Child Nutrition, 17(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.13172
Roy, T. B., Das, T., Das, P., & Das, P. (2023). Analyzing determinants from both compositional and contextual level impeding desired linear growth of children in Indian context. BMC Nutrition, 9(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-023-00725-w
Saaka, M., Saapiire, F. N., & Dogoli, R. N. (2021). Independent and joint contribution of inappropriate complementary feeding and poor water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) practices to stunted child growth. Journal of Nutritional Science, 10. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2021.103
Sahiledengle, B., Petrucka, P., Kumie, A., Mwanri, L., Beressa, G., Atlaw, D., Tekalegn, Y., Zenbaba, D., Desta, F., & Agho, K. E. (2022). Association between water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) and child undernutrition in Ethiopia: a hierarchical approach. BMC Public Health, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14309-z
Sanin, K. I., Haque, A., Nahar, B., Mahfuz, M., Khanam, M., & Ahmed, T. (2022). Food Safety Practices and Stunting among School-Age Children—An Observational Study Finding from an Urban Slum of Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138044
Sewenet, T., W/Selassie, M., Zenebe, Y., Yimam, W., & Woretaw, L. (2022). Undernutrition and Associated Factors Among Children Aged 6–23 Months in Dessie Town, Northeastern Ethiopia, 2021: A Community Based Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2022.916726
Sinharoy, S. S., Schmidt, W.-P., Cox, K., Clemence, Z., Mfura, L., Wendt, R., Boisson, S., Crossett, E., Grépin, K. A., Jack, W., Condo, J., Habyarimana, J., & Clasen, T. (2016). Child diarrhoea and nutritional status in rural Rwanda: a cross-sectional study to explore contributing environmental and demographic factors. Tropical Medicine & International Health : TM & IH, 21(8), 956–964. https://doi.org/10.1111/tmi.12725
Sisay, M., Atenafu, A., Hunegnaw, M. T., & Lorato, M. M. (2022). Prevalence and factors associated with stunting and thinness among school age children in rural primary schools, East Dembia District, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Nutrition, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-022-00624-6
Soofi, S. B., Khan, A., Kureishy, S., Hussain, I., Habib, M. A., Umer, M., Ariff, S., Sajid, M., Rizvi, A., Ahmed, I., Iqbal, J., Ahmed, K. M., Achakzai, A. B. K., & Bhutta, Z. A. (2023). Determinants of Stunting among Children under Five in Pakistan. Nutrients, 15(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153480
Tariq, J., Sajjad, A., Zakar, R., Zakar, M. Z., & Fischer, F. (2018). Factors associated with undernutrition in children under the age of two years: Secondary data analysis based on the Pakistan demographic and health survey 2012–2013. Nutrients, 10(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060676
Terfa, Z. G., Ahmed, S., Khan, J., & Niessen, L. W. (2022a). Household Microenvironment and Under-Fives Health Outcomes in Uganda: Focusing on Multidimensional Energy Poverty and Women Empowerment Indices. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116684
Terfa, Z. G., Ahmed, S., Khan, J., & Niessen, L. W. (2022b). Household Microenvironment and Under-Fives Health Outcomes in Uganda: Focusing on Multidimensional Energy Poverty and Women Empowerment Indices. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116684
Thahir, A. I. A., Li, M., Holmes, A., & Gordon, A. (2023). Exploring Factors Associated with Stunting in 6-Month-Old Children: A Population-Based Cohort Study in Sulawesi, Indonesia. Nutrients, 15(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153420
Torlesse, H., Cronin, A. A., Sebayang, S. K., & Nandy, R. (2016). Determinants of stunting in Indonesian children: Evidence from a cross-sectional survey indicate a prominent role for the water, sanitation and hygiene sector in stunting reduction. BMC Public Health, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3339-8
Vilcins, D., Sly, P. D., & Jagals, P. (2018). Environmental risk factors associated with child stunting: A systematic review of the literature. Annals of Global Health, 84(4), 551–562. https://doi.org/10.29024/aogh.2361
Vita, M. V. De, Scolfaro, C., Santini, B., Lezo, A., Gobbi, F., Buonfrate, D., Kimani-murage, E. W., Macharia, T., Wanjohi, M., Rovarini, J. M., & Morino, G. (2019). Malnutrition , morbidity and infection in the informal settlements of Nairobi , Kenya : an epidemiological study. 0, 1–11.
Waller, A., Lakhanpaul, M., Godfrey, S., & Parikh, P. (2020). Multiple and complex links between babyWASH and stunting: An evidence synthesis. Journal of Water Sanitation and Hygiene for Development, 10(4), 786–805. https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2020.265
Wicaksono, R. A., Arto, K. S., Mutiara, E., Deliana, M., Lubis, M., & Batubara, J. R. L. (2021). Risk factors of stunting in indonesian children aged 1 to 60 months. Paediatrica Indonesiana(Paediatrica Indonesiana), 61(1), 12–19. https://doi.org/10.14238/pi61.1.2021.12-9
Widyaningsih, F., Mulyaningsih, T., Rahmawati, F. N., & Adhitya, D. (2018). Determinants of Socioeconomic and Rural-Urban Disparities in Stunting Evidence from Indonesia. Rural and Remote Health, 18(October 2016), 1–13.
Woldesenbet, B., Tolcha, A., & Tsegaye, B. (2023). Water, hygiene and sanitation practices are associated with stunting among children of age 24-59 months in Lemo district, South Ethiopia, in 2021: community based cross sectional study. BMC Nutrition, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-023-00677-1
Wolf, J., Johnston, R. B., Ambelu, A., Arnold, B. F., Bain, R., Brauer, M., Brown, J., Caruso, B. A., Clasen, T., Colford, J. M., Mills, J. E., Evans, B., Freeman, M. C., Gordon, B., Kang, G., Lanata, C. F., Medlicott, K. O., Prüss-Ustün, A., Troeger, C., … Cumming, O. (2023). Burden of disease attributable to unsafe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene in domestic settings: a global analysis for selected adverse health outcomes. The Lancet, 401(10393), 2060–2071. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00458-0
Woodruff, B. A., Wirth, J. P., Ngnie-Teta, I., Beaulière, J. M., Mamady, D., Ayoya, M. A., & Rohner, F. (2018). Determinants of Stunting, Wasting, and Anemia in Guinean Preschool-Age Children: An Analysis of DHS Data From 1999, 2005, and 2012. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 39(1), 39–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/0379572117743004
Yani, D. I., Rahayuwati, L., Sari, C. W. M., Komariah, M., & Fauziah, S. R. (2023). Family Household Characteristics and Stunting: An Update Scoping Review. Nutrients, 15(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010233
Yunitasari, E., Lee, B. O., Krisnana, I., Lugina, R., Solikhah, F. K., & Aditya, R. S. (2022). Determining the Factors That Influence Stunting during Pandemic in Rural Indonesia: A Mixed Method. Children, 9(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/children9081189
Yushananta, P., & Ahyanti, M. (2022). Risk Factors of Stunting in ChildrenAged 6–59 Months: ACase-Control Study in Horticulture Area. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 10(E), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2022.7768