Relationship Between Demographic Characteristics and Central Obesity with Dyslipidemia among Adult Population in Indonesia
https://doi.org/10.33860/bpk.v53i2.4018
Keywords:
dyslipidemia, adults, central obesity, demographic characteristicsAbstract
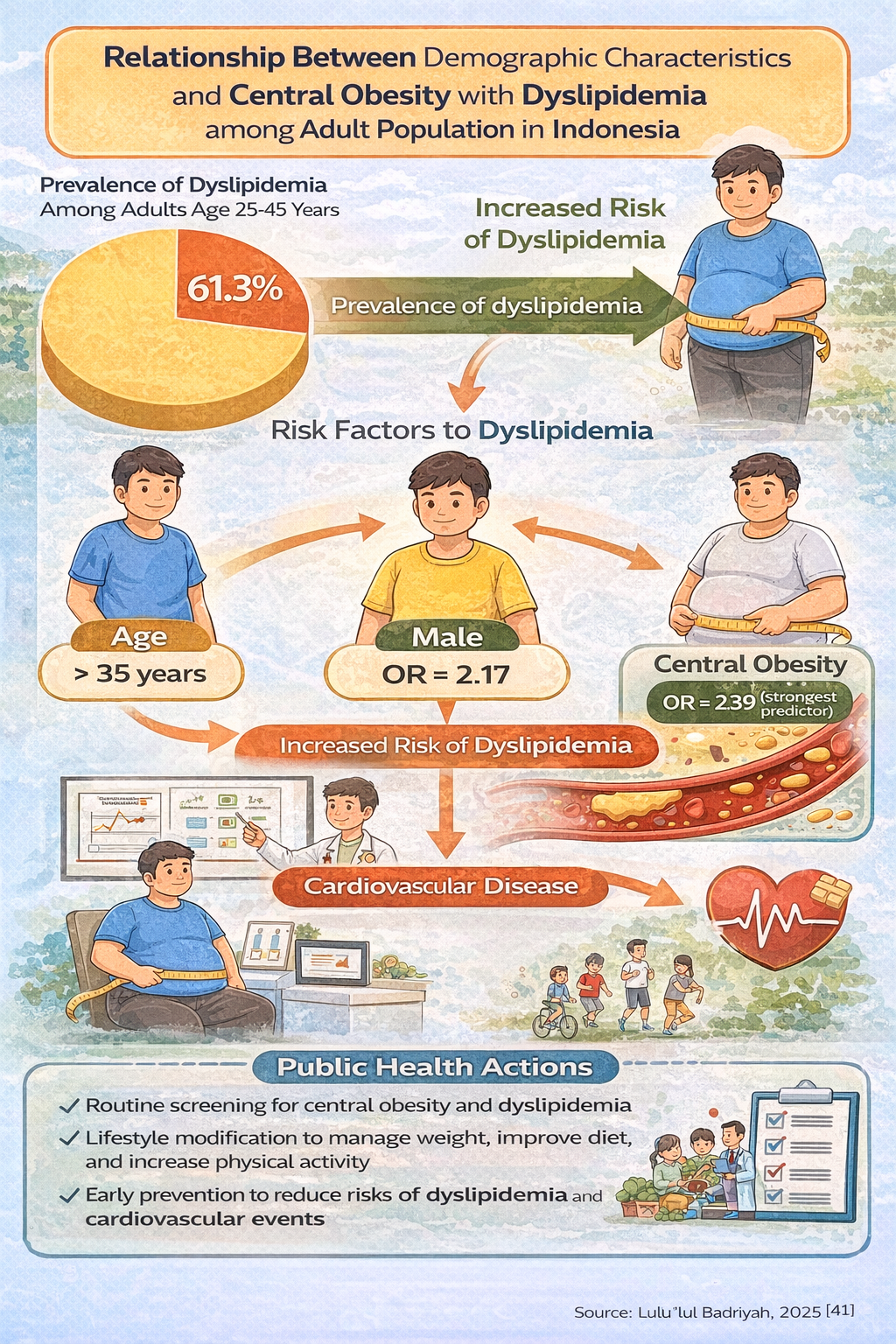
Background: One of the main risk factors for cardiovascular disease and the leading cause of death worldwide, including in Indonesia, is dyslipidemia. The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between demographic characteristics and central obesity with dyslipidemia among adults in Indonesia.
Methods: This study used national Basic Health Research data from 2018. Study design is cross sectional. This study was conducted in September 2024. The study population consisted of individuals aged 25–45 years in Indonesia. Initially, the sample size included 305,457 respondents, but after data cleaning, 12,796 respondents with complete data remained. The analysis was conducted univariately using frequency distribution and percentages, bivariately using chi-square tests, and multivariately using multiple logistic regression.
Results: The results of bivariate analysis showed a significant relationship between age (p=0.000, OR=1.46), gender (p=0.000, OR=1.53), central obesity (p=0.000, OR=1.79) and dyslipidemia. There was no relationship between level of education and dyslipidemia (p=0.283). Central obesity showed the strongest association in multivariate analysis
Conclusion: In conclusion, the variables associated with dyslipidemia are age, gender, and central obesity. Central obesity emerged as the strongest predictor of dyslipidemia in the multivariate analysis. Management of central obesity such as dietary improvements and increased physical activity should be considered to decrease risk of dyslipidemia.
Downloads
References
Ali, H. I., Elmi, F., Stojanovska, L., Ibrahim, N., Cheikh Ismail, L., & Al Dhaheri, A. S. (2022). Associations of Dyslipidemia with Dietary Intakes, Body Weight Status and Sociodemographic Factors among Adults in the United Arab Emirates. Nutrients, 14(16). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163405
Berberich, A. J., & Hegele, R. A. (2022). A Modern Approach to Dyslipidemia. Endocrine Reviews, 43(4), 611–653. https://doi.org/10.1210/endrev/bnab037
Dai, H., Liu, C., Li, P., Mai, Z., Tan, X., Chen, S., Zhou, Z., Tang, Z., Miao, J., Liu, L., & Fang, Y. (2020). Risk of Dyslipidemia Associated with VEGF/VEGFR Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis. Translational Oncology, 13(6), 100779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100779
Ebrahimi, H., Emamian, M. H., Hashemi, H., & Fotouhi, A. (2016). Dyslipidemia and its risk factors among urban middle-aged Iranians: A population-based study. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews, 10(3), 149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2016.01.009
Gebreegziabiher, G., Belachew, T., Mehari, K., & Tamiru, D. (2021). Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among adult residents of Mekelle City, Northern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE, 16(2 February), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0243103
Graham, I. M., Catapano, A. L., & Wong, N. D. (2017). Current guidelines on prevention with a focus on dyslipidemias. Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy, 7(2), S4–S10. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt.2017.04.04
Kamso, S. (2007). Dislipidemia dan Obesitas Sentral pada Lanjut Usia di Kota Padang. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Nasional, 2(2), 73–77. https://doi.org/10.21109/kesmas.v2i2.274%0A
Katulanda, P., Dissanayake, H. A., De Silva, S. D. N., Katulanda, G. W., Liyanage, I. K., Constantine, G. R., Sheriff, R., & Matthews, D. R. (2018). Prevalence, patterns, and associations of dyslipidemia among Sri Lankan adults—Sri Lanka Diabetes and Cardiovascular Study in 2005–2006. Journal of Clinical Lipidology, 12(2), 447–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacl.2018.01.006
Kemenkes. (2013). Riset Kesehatan Dasar (RISKESDAS) 2013. In Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Departemen Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. https://doi.org/1 Desember 2013
Kemenkes. (2018). Riset Kesehatan Dasar (RISKESDAS) 2018.
Koliaki, C., Liatis, S., & Kokkinos, A. (2019). Obesity and cardiovascular disease: revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 92, 98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.10.011
Kusteviani, F. (2015). Faktor yang Berhubungan dengan Obesitas Abdominal pada Usia Produktif (15-64 Tahun) di Kota Surabaya. Jurnal Berkala Epidemiologi, 3(1), 45–56.
Lee, J. S., Chang, P. Y., Zhang, Y., Kizer, J. R., Best, L. G., & Howard, B. V. (2017). Triglyceride and HDL-C dyslipidemia and risks of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke by glycemic dysregulation status: The strong heart study. Diabetes Care, 40(4), 529–537. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-1958
Lee, Y. ho, Lee, S. G., Lee, M. H., Kim, J. H., Lee, B. W., Kang, E. S., Lee, H. C., & Cha, B. S. (2014). Serum cholesterol concentration and prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the korea national health and nutrition examination surveys 2008-2010: Beyond the tip of the iceberg. Journal of the American Heart Association, 3(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.113.000650
Listiyana, A. D., Mardiana, & Prameswari, G. N. (2013). Obesitas Sentral Dan Kadar Kolesterol Darah Total. KESMAS - Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat, 9(1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.15294/kemas.v9i1.2828
Lu, Y., Hajifathalian, K., Ezzati, M., Woodward, M., Rimm, E. B., Danaei, G., Selmer, R., Strand, B. H., Dobson, A., Hozawa, A., Nozaki, A., Okayama, A., Rodgers, A., Tamakoshi, A., Zhou, B. F., Zhou, B., Yao, C. H., Jiang, C. Q., Gu, D. F., … Feskens, E. J. (2014). Metabolic mediators of the effects of body-mass index, overweight, and obesity on coronary heart disease and stroke: A pooled analysis of 97 prospective cohorts with 1·8 million participants. The Lancet, 383(9921), 970–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61836-X
Perkeni. (2021). Pengelolaan Dislipidemia Di Indonesia 2021. PB Perkeni, 1–2.
Pikula, A., Beiser, A. S., Wang, J., Himali, J. J., Kelly-Hayes, M., Kase, C. S., Yang, Q., Seshadri, S., & Wolf, P. A. (2015). Lipid and lipoprotein measurements and the risk of ischemic vascular events: Framingham Study. Neurology, 84(5), 472–479. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001202
Puspitasari, N. (2018). Kejadian Obesitas Sentral pada Usia Dewasa. HIGEIA (Journal of Public Health Research and Development), 2(2), 249–259. https://doi.org/10.15294/higeia.v2i2.21112
Qi, L., Ding, X., Tang, W., Li, Q., Mao, D., & Wang, Y. (2015). Prevalence and risk factors associated with dyslipidemia in Chongqing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(10), 13455–13465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121013455
Sangrós, F. J., Torrecilla, J., Giráldez-García, C., Carrillo, L., Mancera, J., Mur, T., Franch, J., Díez, J., Goday, A., Serrano, R., García-Soidán, F. J., Cuatrecasas, G., Igual, D., Moreno, A., Millaruelo, J. M., Carramiñana, F., Ruiz, M. A., Pérez, F. C., Iriarte, Y., … Regidor, E. (2018). Association of General and Abdominal Obesity With Hypertension, Dyslipidemia and Prediabetes in the PREDAPS Study. Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition), 71(3), 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rec.2017.04.035
Sutanto, K., & Karjadidjaja, I. (2019). Hubungan antara obesitas sentral dengan kejadian dislipidemia pada karyawan Universitas Tarumanagara pengunjung poliklinik Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Tarumanagara November 2016 - April 2017. Tarumanagara Medical Journal, 1(2), 352–360.
Syafiq, A., Badriyah, L., & Fikawati, S. (2020). Perbedaan Status Gizi dan Kesehatan Pralansia dan Lansia di Puskesmas Cipayung Depok. Nutrition and Food Research, 43(2), 89–100.
Vekic, J., Zeljkovic, A., Stefanovic, A., Jelic-Ivanovic, Z., & Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. (2019). Obesity and dyslipidemia. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 92, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.005
Widyasari, N. (2017). Hubungan karakteristik responden dengan risiko diabetes melitus dan dislipidemia Kelurahan Tanah Kalikedinding. Jurnal Unair, 5(1), 131–141. https://doi.org/10.20473/jbe.v5i1.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2016). Raised Cholesterol. In World Health Organisation (WHO) (Vol. 17, p. 1).
Xi, Y., Niu, L., Cao, N., Bao, H., Xu, X., Zhu, H., Yan, T., Zhang, N., Qiao, L., Han, K., Hang, G., Wang, W., & Zhang, X. (2020). Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors among adults aged ≥35 years in northern China: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 20(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09172-9