A Multivariate Prediction Model for Hypertension Incidence
https://doi.org/10.33860/jik.v19i1.4039
Keywords:
Hypertension, Body Mass Index (BMI), family history of hypertension, prediction modelAbstract
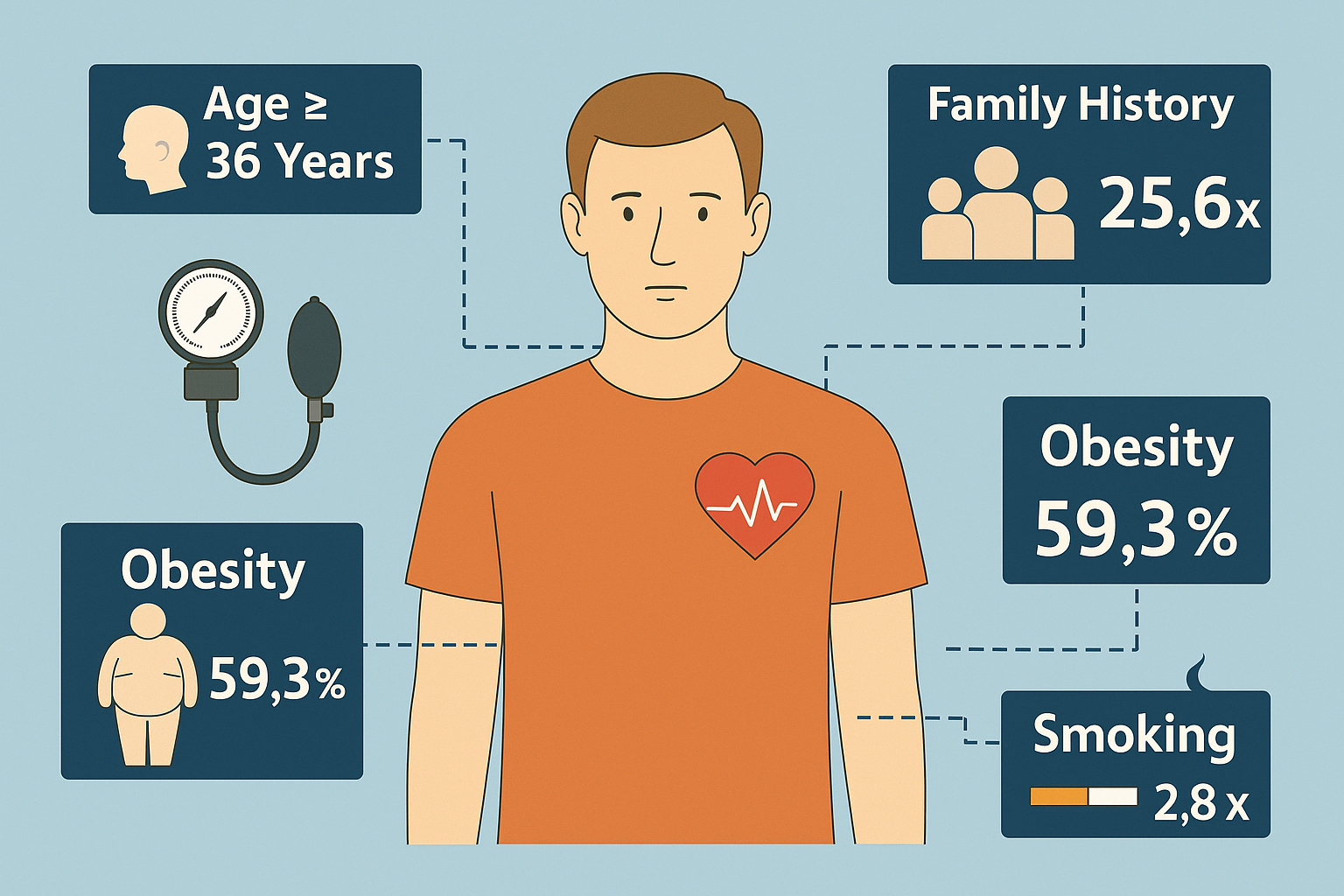
Hypertension is a major global non-communicable disease and a leading cause of premature death. This study aimed to develop a multivariate prediction model for hypertension incidence in the Banggai Community Health Center working area, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. An analytical observational study with a case-control design was conducted involving 140 people, equally divided into case and control groups. Data were collected on age, family history of hypertension, obesity status, smoking status, coffee consumption habits, use of hormonal birth control, and place of residence. Univariate, bivariate, and multivariate analyses were performed. The final regression model included sex, age, family history of hypertension, body mass index (BMI), and smoking status, which together could predict hypertension incidence by 59.3%. Family history of hypertension was the most dominant variable, with those having a history being 25.6 times more likely to develop hypertension than those without a history (p < 0.001). Age ≥ 36 years, obesity, and smoking were also significant risk factors. The prediction model is useful for assessing individual hypertension risk and guiding early diagnosis and treatment. Family-based health education and screening for non-communicable diseases based on the prediction variables are recommended to reduce hypertension prevalence. Future research should consider prospective designs, involve more samples, and include additional variables such as diet, physical activity, and stress level to enhance the model's predictive accuracy.
References
1. WHO. Hypertension [Internet]. 2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
2. Natalia Tambunan L, Prilelli Baringbing E, Eka Harap S, Raya P, Tengah K. The Relationship Of Characteristics With The Event Of Hypertension In Outpatient Patients In RSUD dr. Doris Sylvanus Central Kalimantan Province. Jurnal Surya Medika (JSM). 2022;8. https://journal.umpr.ac.id/index.php/jsm/article/view/4511
3. BKPK RI. Survei Kesehatan Indonesia Dalam Angka. Jakarta; 2023. https://www.badankebijakan.kemkes.go.id/ski-2023-dalam-angka/
4. Candra IW. Pengaruh Relaksasi Progresif Dan Meditasi Terhadap Tingkat Stres Pasien Hipertensi. Jurnal Riset Kesehatan Nasional. 2019;1(2). https://ejournal.itekes-bali.ac.id/index.php/jrkn/article/view/46
5. Marbun WS, Hutapea LMN. Penyuluhan Kesehatan pada Penderita Hipertensi Dewasa terhadap Tingkat Pengetahuan Hipertensi. Jurnal Keperawatan Silampari. 2022;6(1). https://journal.ipm2kpe.or.id/index.php/JKS/article/view/4170
6. Kurdi F, Sunaryo MMF, Romadhonia F, Amini DA, Ramadhan K. CERDIK Behavior in Elderly with Hypertension During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Perilaku “CERDIK” Pada Lansia Dengan Hipertensi Selama Pandemi COVID-19. Jurnal Kesehatan Komunitas Indonesia. 2022;2(1 SE-Articles). https://ebsina.or.id/journals/index.php/jkki/article/view/2
7. Asri IP, Salamah NP, Putri AM, Khairunnisa A, Afifah F, Kusumastuti I. Analisis Faktor Risiko Kejadian Hipertensi di Wilayah Kota Depok: Analysis of Risk Factors for Hypertension in the Kota Depok. Journal of Public Health Education. 2022;1(3). https://journals.prosciences.net/index.php/JPHE/article/view/51
8. American Heart Association. Correction to: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report from the American Heart Association (Circulation (2017) 135 (e146-e603) DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485). Vol. 135, Circulation. 2017. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000491
9. Ihsan Kurniawan S. Hubungan Olahraga, Stress dan Pola Makan dengan Tingkat Hipertensi di Posyandu Lansia di Kelurahan Sudirejo I Kecamatan Medan Kota . Journal of Health Science and Physiotherapy. 2019;1(1). https://www.neliti.com/publications/274147/hubungan-olahraga-stress-dan-pola-makan-dengan-tingkat-hipertensi-di-posyandu-la
10. Black JM, Hawks JH. Keperawatan Medikal Bedah : Dasar-Dasar Keperawatan Medikal Bedah. Jakarta: EGC. 2023.
11. Mamuaya SK, Asrifuddin A, Kalesaran AFC. Faktor-faktor yang berhubungan dengan kejadian hipertensi pada lansia di Desa Kali Kecamatan Pineleng Kabupaten Minahasa Tahun 2017. Media Kesehatan. 2017;9(1).
12. Wise IA, Charchar FJ. Epigenetic modifications in essential hypertension. Vol. 17, International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4848907/
13. Singh M, Singh AK, Pandey P, Chandra S, Singh KA, Gambhir IS. Molecular genetics of essential hypertension. Vol. 38, Clinical and Experimental Hypertension. 2016. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27028574/
14. Padmanabhan S, Dominiczak AF. Genomics of hypertension: the road to precision medicine. Vol. 18, Nature Reviews Cardiology. 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41569-020-00466-4
15. Dodoo SN, Benjamin IJ. Genomic Approaches to Hypertension. Vol. 35, Cardiology Clinics. 2017. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28411893/
16. Kusumayanti E, Maharani, Filma A, Suci S. Faktor-Faktor yang berhubungan dengan kejadian Hipertensi Usia Produktif di Desa Pulau Jambu Wilayah Kerja UPTD Puskesmas Kuok Tahun 2020. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2021;14(1). https://journal.universitaspahlawan.ac.id/index.php/ners/article/view/1672
17. Hamzah A, Khasanah U, Norviatin D. The Correlation of Age, Gender, Heredity, Smoking Habit, Obesity, and Salt Consumption with Hypertension Grade in Cirebon, Indonesia. GHMJ (Global Health Management Journal). 2019;3(3). https://publications.inschool.id/index.php/ghmj/article/view/586
18. Widjaya N, Anwar F, Laura Sabrina R, Rizki Puspadewi R, Wijayanti E. The Association Between Age and Incidences of Hypertention in Kresek District And Tegal Angus District, Tangerang Regency. Jurnal Kedokteran Yarsi. 2018;26(3). https://academicjournal.yarsi.ac.id/index.php/jky/article/view/756
19. Anggara FHD, Prayitno N. Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Tekanan Darah di Puskesmas Telaga Murni Cikarang Barat Tahun 2012. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan. 2013;5(1). https://fmipa.umri.ac.id/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/ELFIKA-FAKTOR-2-YG-B.D-PD-TENSI.pdf
20. Yunus M, Aditya IWC, Eksa DR. Hubungan Usia Dan Jenis Kelamin Dengan Kejadian Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Haji Pemanggilan Kecamatan Anak Tuha Kab. Lampung Tengah. Jurnal Ilmu Kedokteran dan Kesehatan. 2021;8(3). https://ejurnalmalahayati.ac.id/index.php/kesehatan/article/view/5193
21. Tjekyan RMS, Zulkarnain M, Sartik S. Faktor - Faktor Risiko Dan Angka Kejadian Hipertensi Pada Penduduk Palembang. Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat. 2017;8(3). https://ejournal.fkm.unsri.ac.id/index.php/jikm/article/view/237
22. Ningsih DLR. Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kejadian Hipertensi Pada Pekerja Sektor Informal di Pasar Beringharjo Kota Yogyakarta. Naskah publikasi. 2017. https://digilib.unisayogya.ac.id/2689/
23. Widia, Made Yudha Ganesa Wikantyas; Sudhana IW. Gambaran Faktor Risiko Hipertensi Pada Masyarakat Pralansia Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Dawan I Periode Mei 2013. Jurnal Medika Udayana. 2015;4(4). https://ojs.unud.ac.id/index.php/eum/article/view/13101/8776
24. Nugraheni A, Mulyani S, Cahyanto EB, Musfiroh M, Sukamto IS. Hubungan Berat Badan Dan Tekanan Darah Pada Lansia. PLACENTUM: Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan dan Aplikasinya. 2019;7(2). https://jurnal.uns.ac.id/placentum/article/view/30518
25. Kembuan IY, Kandou G, Kaunang WPJ. Hubungan Obesitas dengan Penyakit Hipertensi pada Pasien Poliklinik Puskesmas Touluaan Kabupaten Minahasa Tenggara. Jurnal Paradigma. 2016;4(2).
26. Natalia D, Hasibuan P, Hendro H. Hubungan Obesitas dengan Hipertensi pada Penduduk Kecamatan Sintang, Kalimantan Barat. eJournal Kedokteran Indonesia. 2015;2(3). https://journal.umpr.ac.id/index.php/jsm/article/view/4511
27. Kartikasari AN. Faktor Risiko Hipertensi pada Masyarakat di Desa Kabongan Kidul, Kabupaten Rembang. Karya Tulis Ilmiah S-1 Kedokteraan Umum Universitas Diponegoro. 2012. https://media.neliti.com/media/publications/115982-ID-faktor-risiko-hipertensi-pada-masyarakat.pdf
28. Retno Taufanntias Puji Ayu Purwanti. Hubungan Kebiasaan Merokok Dengan Terjadinya Hipertensi Pada Pegawai CV Lusindo Desa Sukadanau Cikarang Barat. Vol. 6, Energies. 2018. https://eprints.ums.ac.id/58223/
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with Poltekita : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License.
Poltekita : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.






