Implementation of The draivCare App on Maternal Health Services
https://doi.org/10.33860/jbc.v7i2.4049
Keywords:
Pregnant women, draivCare, mhealth app, antenatal care servicesAbstract
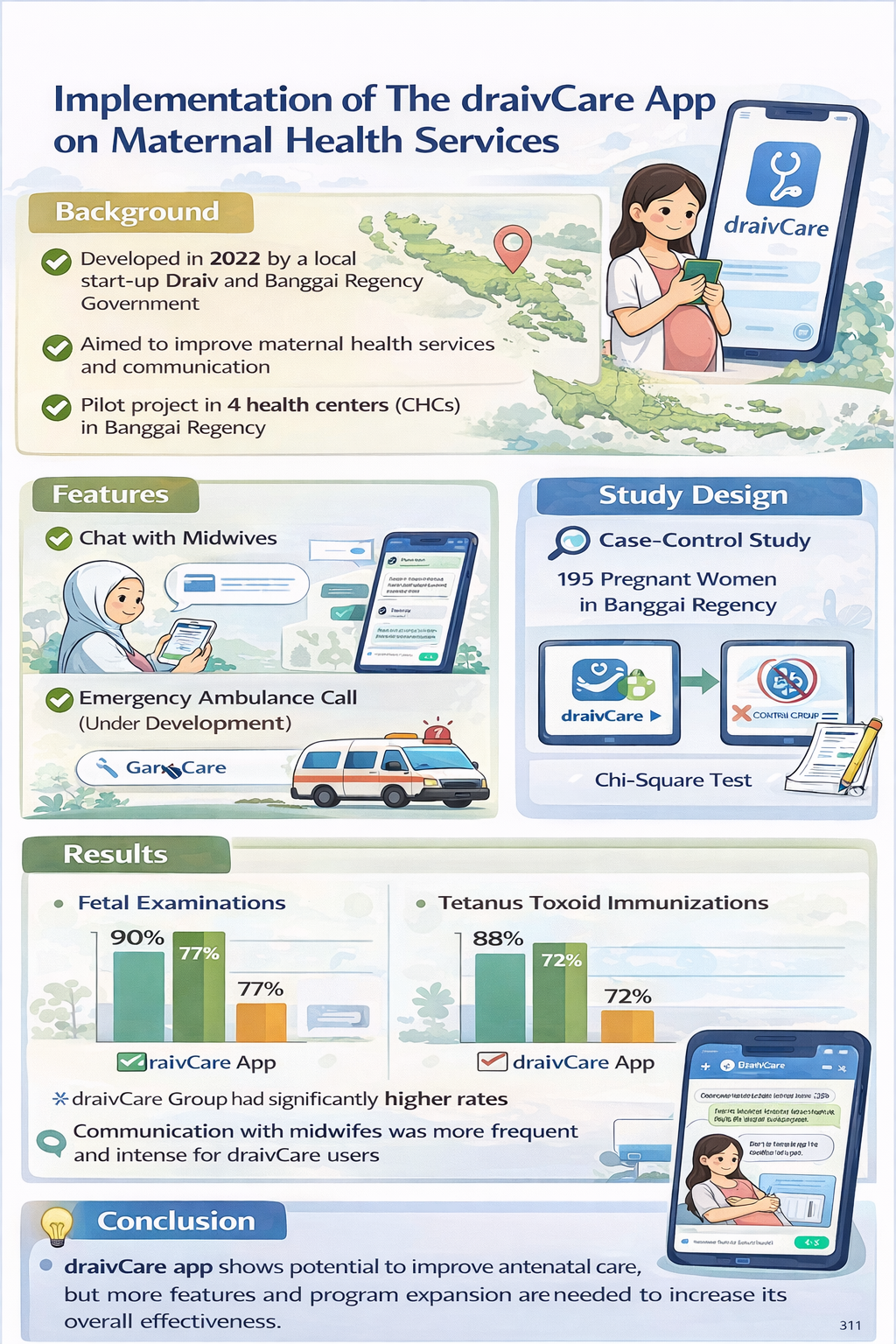
Background: Banggai Regency government collaborated with a local start-up, Draiv, to develop a health service app specialized for pregnant women, called draivCare. This study aims to evaluate the effect of draivCare utilization on maternal health services. Methods: This is a case-control method to identify the differentiation of ANC services utilization during the pregnancy period between groups. We use secondary data and conducting interview with midwives. A total 39 pregnant women who use draivCare app in their pregnancy were administered to the intervention(case) group, whereas 156 pregnant women who did not use draivCare app in their pregnancy belong to the control group. Antenatal care (ANC) frequency and components were the variables studied using chi-square. Results: The proportion of mother who received the fetal examination and the proportion of mothers who received tetanus toxoid immunization are significantly differ between groups. Despite the barriers such as android-based mobile phone ownership of the mothers, the communication between pregnant women and midwives is quite intense. Conclusion: The implementation of draivCare app has yet to affect pregnant women’s health care quality and quantity significantly. However, the intense communication between pregnant women and midwives shows a potential effect of the app on improving antenatal care.
Downloads
References
Amanda, G., & Layman, C. V. (2022). Examining the Intention to Use Mobile Health Applications Amongst Indonesians. Milestone: Journal of Strategic Management, 2(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.19166/ms.v2i2.5924
Amoakoh-Coleman, M., Borgstein, A. B. J., Sondaal, S. F. V., Grobbee, D. E., Miltenburg, A. S., Verwijs, M., … Klipstein-Grobusch, K. (2016). Effectiveness of mHealth interventions targeting health care workers to improve pregnancy outcomes in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 18(8), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.5533
Aurelia, A., Diah, P., & Care, A. (2022). Determinants of Antenatal Care for Pregnant Women in Healthcare Facilities during the Covid-19 Pandemic : A Systematic Review. Journal of Health Science and Prevention, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.29080/jhsp.v6i1.613
Denny, H. M., Laksono, A. D., Matahari, R., & Kurniawan, B. (2022). The Determinants of Four or More Antenatal Care Visits Among Working Women in Indonesia. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health, 34(1), 51–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/10105395211051237
Dinas Kesehatan Kabupaten Banggai. (2019). Profil Dinas Kesehatan Kabupaten Banggai 2019. Kab. Banggai.
Dinas Kesehatan Kabupaten Banggai. (2020). Profil Kesehatan Dinas Kabupaten Banggai 2020. Kabupaten Banggai.
Eberle, C., Loehnert, M., & Stichling, S. (2021). Effectivness of specific mobile health applications (mHealth-apps) in gestational diabtetes mellitus: a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, 21(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-021-04274-7
Kante, M., & Målqvist, M. (2025). Effectiveness of SMS-based interventions in enhancing antenatal care in developing countries: a systematic review. BMJ Open, 15(2), e089671. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089671
Kassa, A., & Matlakala, M. C. (2022). Effectiveness of mHEALTH Application at Primary Health Care to Improve Maternal and New-born Health Services in Rural Ethiopia: Comparative study. MedRxiv, 21, 2022.04.02.22272628. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.02.22272628
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Peraturan Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Nomor 97 Tahun 2014 tentang Pelayanan Kesehatan Masa Sebelum Hamil, Masa Hamil, Persalinan, dan Masa Sesudah Melahirkan, Penyelenggaraan Pelayana Kontrasepsi, Serta Pelayanan Kesehatan Seksual. , (2014). Indonesia.
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. (2020). Pedoman pelayanan antenatal, persalinan, nifas, dan bayi baru lahir di Era Adaptasi Kebiasaan Baru. Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Kesehatan Masyarakat. Retrieved from https://dinkes.jatimprov.go.id/userimage/dokumen/revisi 2.pdf
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. (2024). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2023. In Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Indonesia. Retrieved from https://www.kemkes.go.id/downloads/resources/download/pusdatin/profil-kesehatan-indonesia/Profil-Kesehatan-2021.pdf
Kwee, V., Istijanto, I., & Widjojo, H. (2022). Understanding the Determinants of m-Health Adoption in Indonesia. Jurnal Manajemen Teori Dan Terapan | Journal of Theory and Applied Management, 15(3), 408–422. https://doi.org/10.20473/jmtt.v15i3.40142
Mandiwa, C., & Namondwe, B. (2024). Assessment of quality of antenatal care services and associated factors in Malawi: Insights from a nationwide household survey. PLOS ONE, 19(6), e0305294. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305294
Murthy, N., Chandrasekharan, S., Prakash, M. P., Ganju, A., Peter, J., Kaonga, N., & Mechael, P. (2020). Effects of an mHealth voice message service (mMitra) on maternal health knowledge and practices of low-income women in India: Findings from a pseudo-randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health, 20(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-08965-2
Olajubu, A. O., Fajemilehin, B. R., Olajubu, T. O., & Afolabi, B. S. (2020). Effectiveness of a mobile health intervention on uptake of recommended postnatal care services in Nigeria. PLoS ONE, 15(9 september), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238911
Oliveira-Ciabati, L., Vieira, C. S., Franzon, A. C. A., Alves, D., Zaratini, F. S., Braga, G. C., … Souza, J. P. (2017). PRENACEL – a mHealth messaging system to complement antenatal care: a cluster randomized trial. Reproductive Health, 14(1), 146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-017-0407-1
Omotosho, A., Sodeinde, K., Abolurin, O., Adekoya, A., & Abiodun, O. (2022). How effective is antenatal care in preparing mothers for newborn care? An exploratory survey of lactating women in a rural Nigerian district. Heliyon, 8(11), e11650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11650
Patel, S. J., Subbiah, S., Jones, R., Muigai, F., Rothschild, C. W., Omwodo, L., … Nour, N. M. (2018). Providing support to pregnant women and new mothers through moderated WhatsApp groups: a feasibility study. MHealth, 4(May), 14–14. https://doi.org/10.21037/mhealth.2018.04.05
Sondaal, S. F. V., Browne, J. L., Amoakoh-Coleman, M., Borgstein, A., Miltenburg, A. S., Verwijs, M., & Klipstein-Grobusch, K. (2016). Assessing the effect of mHealth interventions in improving maternal and neonatal care in low- And middle-income countries: A systematic review. PLoS ONE, 11(5). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154664
Syahriani, M. N., Mufdlilah, & Sulistyaningsih. (2022). Analisis Pelaksanaan ANC Terpadu pada masa Pandemi COvid-19 di Puskesmas Kalasan. Jurnal Kesehatan Manarang, 8(1), 26–35. https://doi.org/10.33490/jkm.v8i1.542
Trisnawati, R. E., Weraman, P., & Manongga, S. P. (2020). Determinant Factors of Visiting Antenatal Care among Pregnant Mothers In Dictor Public Health Center, Manggarai Regency. International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS), 4(1), 42–51. Retrieved from https://ijnhs.net/index.php/ijnhs/article/view/381
UNICEF. (2023). Never Forgotten: The situation of stillbirth around the globe. New York. Retrieved from https://data.unicef.org/resources/never-forgotten-stillbirth-estimates-report/
Wang, Y., Xue, H., Huang, Y., Huang, L., & Zhang, D. (2017). A Systematic Review of Application and Effectiveness of mHealth Interventions for Obesity and Diabetes Treatment and Self-Management. Advances in Nutrition, 8(3), 449–462. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.014100
Ward, V. C., Raheel, H., Weng, Y., Mehta, K. M., Dutt, P., Mitra, R., … Darmstadt, G. L. (2020). Impact Of Mhealth Interventions for Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn and Child Health and Nutrition at Scale: Bbc Media Action and The Ananya Program in Bihar, India. Journal of Global Health, 10(2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.10.021005
Wardaya, E. C. E., Martini, M., Sutiningsih, D., & Hestiningsih, R. (2024). Pola Hubungan Kepercayaan Dengan Penolakan Imunisasi Dasar Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Tembarak. Jurnal Riset Kesehatan Masyarakat, 4(1), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.14710/jrkm.2024.22164
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dian Kurniasari Yuwono, Yustianty Monoarfa, Nitro Galenso (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Jurnal Bidan Cerdas agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.




