Effectiveness of Audio-Visual Media on the Four Aspects of Complementary Feeding Education in Pregnant Women to Prevent Stunting
https://doi.org/10.33860/jbc.v7i2.3068
Keywords:
audio visual, knowlegde, attitude, stunting, leafletsAbstract
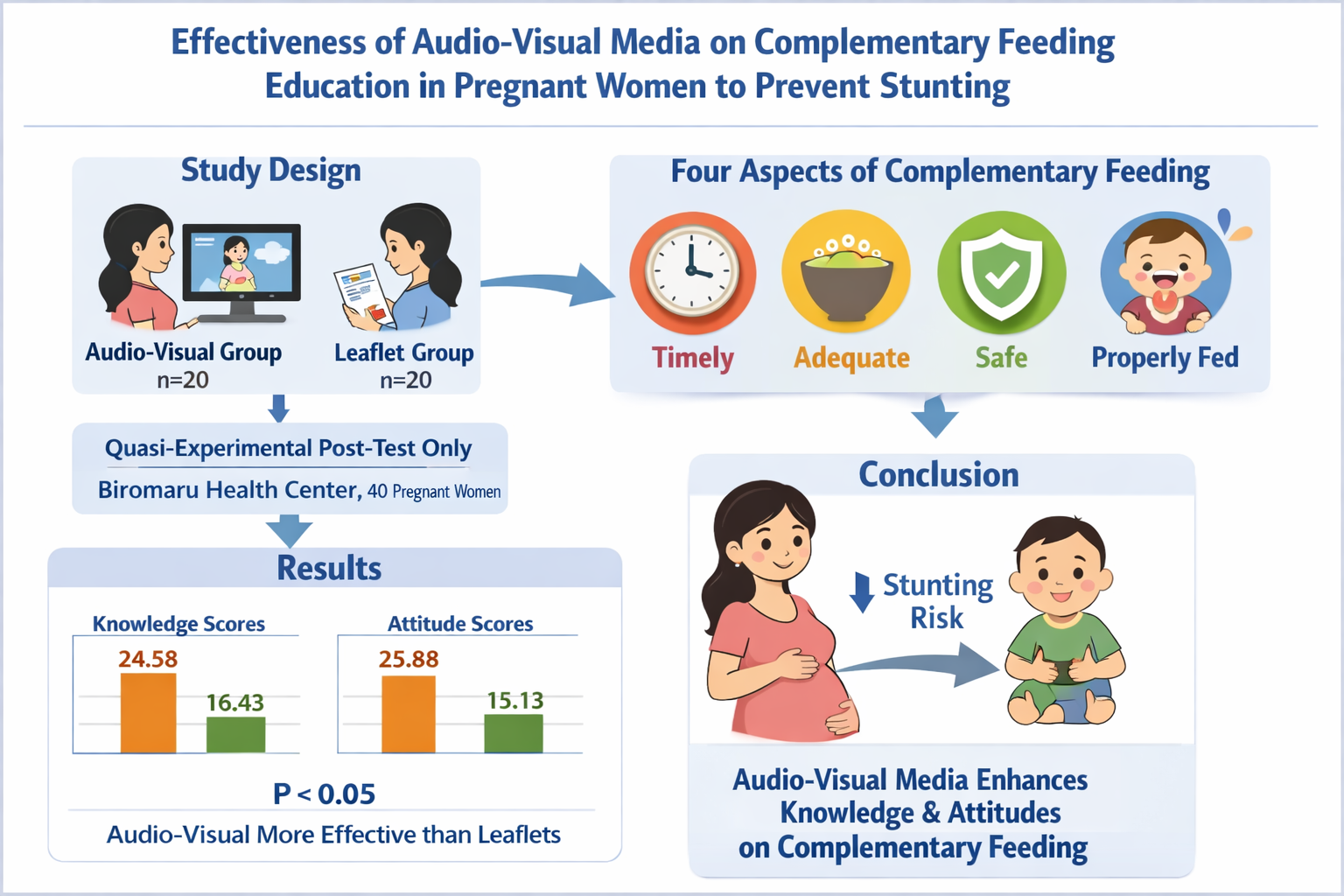
Background: Indonesia has the third-highest stunting rate in Southeast Asia, with inadequate of complementary feeding contributing to the issue. Enhancing pregnant women's knowledge and attitudes about proper complementary feeding is crucial, and research shows that audio-visual media is more effective for education than other formats. This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of audio-visual educational media and leaflets in educating pregnant women about the four conditions (namely timely, adequate, safe, and properly fed) for giving complementary feeding. Methods: This study utilized a quasi-experimental design with a post-test-only control group. Data was collected from 40 Biromaru Community Health Center pregnant women from August to September 2023. The analysis utilized frequency distribution and the Mann-Whitney test. Results: The average knowledge (24.58) and attitude (25.88) of the audio-visual media group was higher than the knowledge (16.43) and attitude (15.13) of the leaflet media group. P value=0.02(<0.05) for the knowledge variable and p=0.01(<0.05) for the attitude variable Conclusion: Audio-visual media is more effective than leaflets in improving knowledge and attitudes about the four complementary feeding requirements to prevent stunting in pregnant women. It can serve as an alternative educational tool for health workers during pregnant women's classes.
Downloads
References
Adhisty, W. A., Immawanti, I., Evawaty, E., Ayu, M., Muzdalia, I., & Latif, A. R. (2023). Pengaruh Penyuluhan berbasis Video terhadap Peningkatan Pengetahuan dan Sikap Ibu tentang Pemberian MP-ASI pada balita 6-24 Bulan. J-HEST Journal of Health Education Economics Science and Technology, 5(2), 296–303. https://doi.org/10.36339/jhest.v5i2.116
Agustini, A. (2014). Promosi Kesehatan. Yogjakarta: Deepublish.
Akombi, B. J., Agho, K. E., Hall, J. J., Wali, N., Renzaho, A. M. N., & Merom, D. (2017). Stunting, wasting and underweight in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080863
Andriani, R., Anggarini, I. A., & Valencia, F. V. (2022). Efektivitas Edukasi Melalui Aplikasi COMPLEMENTARY FEEDING terhadap Pengetahuan Ibu. Jurnal Delima Harapan, 9(1), 59–70. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31935/delima.v9i1.151
Ariani, M. (2020). Determinan Penyebab Kejadian Stunting Pada Balita: Tinjauan Literatur. Dinamika Kesehatan: Jurnal Kebidanan Dan Keperawatan, 11(1), 172–186. https://doi.org/10.33859/dksm.v11i1.559
Black, R. E., Victoria, C. G., Walker, S. P., Bhutta, Z. A., Christian, P., Onis, M., … Uauy, R. (2013). Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet, 382(9890), 427–451. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60937-X
IDAI. (2015). Rekomendasi Praktik Pemberian Makan Berbasis Bukti pada Bayi dan Batita di Indonesia untuk Mencegah Malnutrisi. UKK Nutrisi Dan Penyakit Metabolik, Ikatan Dokter Anak Indonesia. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
IEG. (2018). Global Nutrition Report - executive summary. Global Nutrition Report, (June), 118. https://globalnutritionreport.org/reports/global-nutrition-report-2018/
Indriani, R., Sendra, E., Rahayu, D. E., & Firdayanti, I. (2023). Media Edukasi dan Promosi Kesehatan. Klaten: Lakeisha.
Ismawati, Winda, & Andriani, K. (2018). Efektifitas Penggunaan Media Leaflet, Buku Saku, Video Untuk Meningkatkan Pengetahuan Pemberian Makanan Pendamping Air Susu Ibu (MP Asi) Di Desa Kenep Kecamatan Sukoharjo. Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta. https://eprints.ums.ac.id/65701/
Kemenkes RI. (2018). Situasi Balta Pendek (stunting) di Indonesia. Pusat Data Kemenkes RI, 301(5), 1163–1178.
Kemenkes RI. (2021). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia Tahun 2020. In Sekretariat Jenderal Kemenkes RI. Jakarta.
Kismul, H., Acharya, P., Mapatano, M. A., & Hatløy, A. (2017). Determinants of childhood stunting in the Democratic Republic of Congo: Further analysis of Demographic and Health Survey 2013-14. BMC Public Health, 18(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-017-4621-0
Koch, N. M., Fione, V. R., Lidya Maramis, J., & Pasambuna, J. (2024). Difference In Using Leaflet And Audio-Visual Media Towards Toothbrushing Knowledge Among Students. JDHT Journal of Dental Hygiene and Therapy, 5(1), 80–86. https://doi.org/10.36082/jdht.v5i1.1517
Lestari, W. (2021). Pendidikan Kesehatan Dengan Media Video Dan Media E Booklet Meningkatkan Pengetahuan Pemberian MP-ASI. 3 no.2(November), 57–66. https://ejournal.poltekkes-smg.ac.id/ojs/index.php/JSK/article/download/7890/2387
Martinez, B., Webb, M. F., Gonzalez, A., Douglas, K., Del Pilar Grazioso, M., & Rohloff, P. (2018). Complementary feeding intervention on stunted Guatemalan children: A randomised controlled trial. BMJ Paediatrics Open, 2(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjpo-2017-000213
Mukhopadhyay, K., Louis, D., Mahajan, G., & Mahajan, R. (2014). Longitudinal Growth of Elbw Neonates. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25228605/
Muthmainah, Nafsiyah, F., Dwiriani, Mati, C., Ekawidyani, & Rahmadia, K. (2015). Pengaruh Penyuluhan Dengan Media Audio Visual Dan Leaflet Terhadap Pengetahuan Ibu Tentang Pemberian Makanan Pendamping Asi. Institut Pertanian Bogor, Bogor. https://repository.ipb.ac.id/handle/123456789/83046
Nirmalasari, N. O. (2020). Stunting Pada Anak : Penyebab dan Faktor Risiko Stunting di Indonesia. Qawwam: Journal For Gender Mainstreming, 14(1), 19–28. https://doi.org/10.20414/Qawwam.v14i1.2372
Nurkhayati, E., Yunarsih, N., Sari, F., Octamelia, M., & Argaheni, N. B. (2022). The Use of Leaflet as A Health Education Media in Increasing The Knowledge of Complementary Feeding for Breastfeeding Mothers. Jurnal Aisyah : Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan, 7(S1), 141–146. https://doi.org/10.30604/jika.v7iS1.1213
Quamme, S. H., & Iversen, P. O. (2022). Prevalence of child stunting in Sub-Saharan Africa and its risk factors. Clinical Nutrition Open Science, 42, 49–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutos.2022.01.009
Rahayuningsih, F. B., & Kristinawati, B. (2023). The Effectiveness Of Audiovisual Media And Leaflets In Enhancing Knowledge, Attitudes, And Practices Of Pregnancy Services. Jurnal Pendidikan Keperawatan Indonesia, 9(2), 193–208. https://ejournal.upi.edu/index.php/JPKI/article/viewFile/68250/pdf
Suhaid, D. N., Sulistiani, R. P., Manungkalit, E. M., & Pabeno, Y. (2022). Pengantar Promosi Kesehatan (Ady. M. Susanto, Ed.). Sukoharjo: Pradina Pustaka.
Susilowati, D. (2016). Promosi Kesehatan. Jakarta Selatan: Pusdik SDM Kesehatan.
Tesfaye, A., & Egata, G. (2021). Stunting and Associated Factors Among Children Aged 6-59 Months From Households in Productive Safety Net Program and Non-productive Safety Net Program in Meta District, East Hararghe Zone, Eastern Ethiopia: a Comparative Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-022-00291-0
Thurstans, S., Sessions, N., Dolan, C., Sadler, K., Cichon, B., Isanaka, S., … Khara, T. (2022). The relationship between wasting and stunting in young children: A systematic review. Maternal and Child Nutrition, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.13246
Tuong, W., Larsen, E. R., & Amstrong, A. W. (2014). Videos to influence: a systematic review of effectiveness of video-based education in modifying health behaviors. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 37(April 2014), 218–233. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-012-9480-7
Utama, L. G., Yuliantini, U., Natan, E., Rizal, O., Wahyudi, A., & Anang. (2021). Pengaruh Media Vidio pada Tingkat Pengetahuan, Sikap dan Perilaku Ibu tentang Balita Stunting di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Tanjung Harapan Kecamatan Ulok Kupai Tahun 2021. Poltekkes Kemenkes Bengkulu, Bengkulu. http://repository.poltekkesbengkulu.ac.id/624/
Uwiringiyimana, V., Ocké, M. C., Amer, S., & Veldkamp, A. (2019). Predictors of stunting with particular focus on complementary feeding practices: A cross-sectional study in the northern province of Rwanda. Nutrition, 60, 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.07.016
Walters, C. N., Rakotomanana, H., Komakech, J. J., & Stoecker, B. J. (2019). Maternal determinants of optimal breastfeeding and complementary feeding and their association with child undernutrition in Malawi (2015-2016). BMC Public Health, 19(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-019-7877-8
Wardhana, E. S., Ratnawati, I. D., Failasufa, H., & Balqis, I. (2023). A Comparative Analysis of the Impact of Audiovisual and Leaflets through Whatsapp as Oral Health Promotion Media on Adolescents’ Knowledge of Oral Health. South Eastern European Journal of Public Health, XXI, 181–188. http://www.seejph.com/index.php/seejph/article/view/453
WHO. (2021). Infant and Young Child Feeding. Retrieved April 13, 2022, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infant-and-young-child-feeding
Windasari, D. P., Syam, I., & Kamal, L. S. (2020). Faktor Hubungan dengan Kejadian Stunting di Puskesmas Tamalate Kota Makassar (Factors related to the incidence of stunting at the Tamalate health center in Makassar city ). Aceh Nutrition Jurnal, 2020(5), 27–34. https://ejournal.poltekkesaceh.ac.id/index.php/an/article/view/193
Yuanrsih, & Rahayu, D. (2017). Perbedaan Pengetahuan Ibu tentang Makanan Pendamping ASI (MP-ASI) dengan Metode Komunikasi Informasi Edukasi (KIE) Menggunakan Media Audio Visual dan Media Visual di Desa Rowoharjo Kecamatan Prambon Kabupaten Nganjuk. Nursing Science Journal, 1(1), 37–44. https://ojs.unik-kediri.ac.id/index.php/nsj/article/view/35
Zogara, A. U., Loaloka, M. S., & Pantaleon, M. G. (2021). Faktor Ibu Dan Waktu Pemberian Complementary feeding Berhubungan Dengan Status Gizi Balita Di Kabupaten Kupang. Journal of Nutrition College, 10(1), 55–61. https://doi.org/10.14710/jnc.v10i1.30246
Zulmiyetri, Safaruddin, & Nurhastuti. (2020). Penulisan Karya ilmiah. Jakarta: Prenada Medika.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yuli Admasari, Sarliana, Linda (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with Jurnal Bidan Cerdas agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International License
You are free to:
- Share, copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.




